OSTEOPATHY
OSTEOPATHYThe osteopathy is a treatment developed by American Dr. Andrew Taylor Still (1828-1917). It is an evaluation and treatment system, with a specific methodology and philosophy, aiming at restoring the body structure and systems, operating by the manual intervention on the tissues (joints, muscles, fascia, ligaments, capsules, viscera, and nervous, vascular and lymphatic tissue).
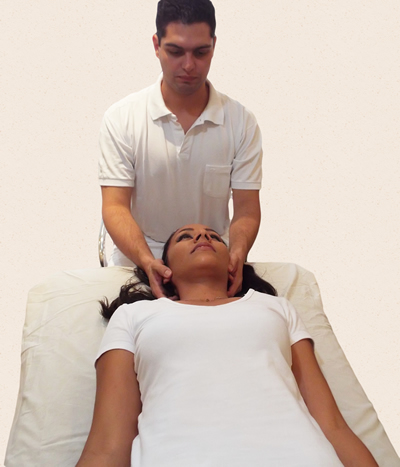
The osteopathy is based on the anatomy, physiology and semiology, as it is a treatment based in a clinical exam. It is highly specific and differentiated treatment, since, by the Manual Therapy, it works on not only bones and muscles, though it also works on less-inspected areas in other techniques, such as the viscera.
There is pain apparently related only to the musculoskeletal system, which may also be related to the viscera, such as the stomach and liver. Considering this different clinical thought, the osteopathy shows excellent results in treating patients.
Within the osteopathy philosophy, the importance given to body natural processes is huge, thus the most part of the osteopathic concepts and their treatment procedures are guided in the central and autonomic nervous system controlling mechanism.
The osteopathy duration is so precise it is recommended and encouraged by the WHO (World Health Organization) as a health practice.
 Call to book an appointment: Tatuapé (11)99697-8452 or (11)94321-1403 / Saúde (11)5589-1628
Call to book an appointment: Tatuapé (11)99697-8452 or (11)94321-1403 / Saúde (11)5589-1628